Introduction
Background
Modern Turkey was founded in 1923 from the remnants of the defeated Ottoman Empire by national hero Mustafa KEMAL, who was later honored with the title Ataturk or "Father of the Turks." Under his leadership, the country adopted radical social, legal, and political reforms. Turkey joined the UN in 1945 and in 1952 it became a member of NATO. In 1963, Turkey became an associate member of the European Community.
Geography
Area
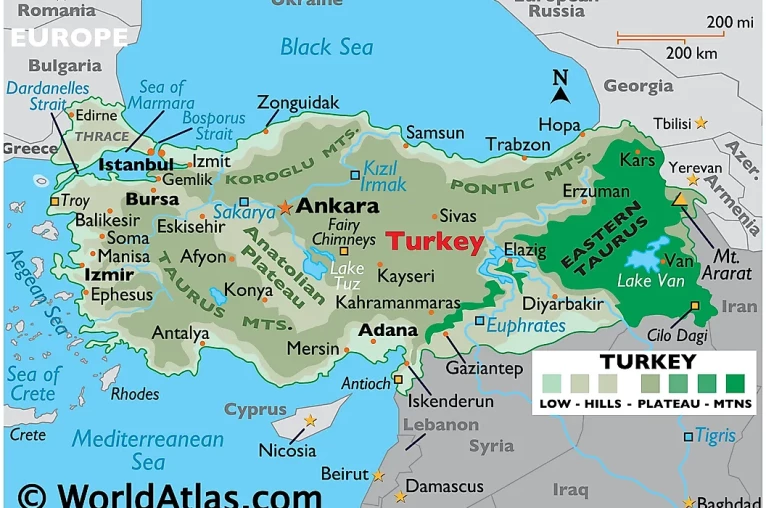
total: 783,562 sq km
land: 769,632 sq km
water: 13,930 sq km
Climate
temperate; hot, dry summers with mild, wet winters; harsher in interior
Natural resources
coal, iron ore, copper, chromium, antimony, mercury, gold, barite, borate, celestite (strontium), emery, feldspar, limestone, magnesite, marble, perlite, pumice, pyrites (sulfur), clay, arable land, hydropower
People and Society
Population
83,047,706 (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Turkish 70-75%, Kurdish 19%, other minorities 6-11% (2016 est.)
Languages
Turkish (official), Kurdish, other minority languages
Religions
Muslim 99.8% (mostly Sunni), other 0.2% (mostly Christians and Jews)
Government
Government type
presidential republic
Capital
name: Ankara
Economy
Economic overview
upper middle-income, diversified Middle Eastern economy; economic instability from 2016 attempted coup and 2018 currency recession; hit hard by COVID-19, increasing poverty and unemployment; endemic corruption; large agriculture labor force
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$2.668 trillion (2021 est.)
Real GDP per capita
$31,500 (2021 est.)
Agricultural products
milk, wheat, sugar beet, tomatoes, barley, maize, potatoes, grapes, watermelons, apples
Industries
textiles, food processing, automobiles, electronics, mining (coal, chromate, copper, boron), steel, petroleum, construction, lumber, paper
Exchange rates
Turkish liras (TRY) per US dollar -
8.85 (2021 est.)



